A shred of advice: How to remove splinters
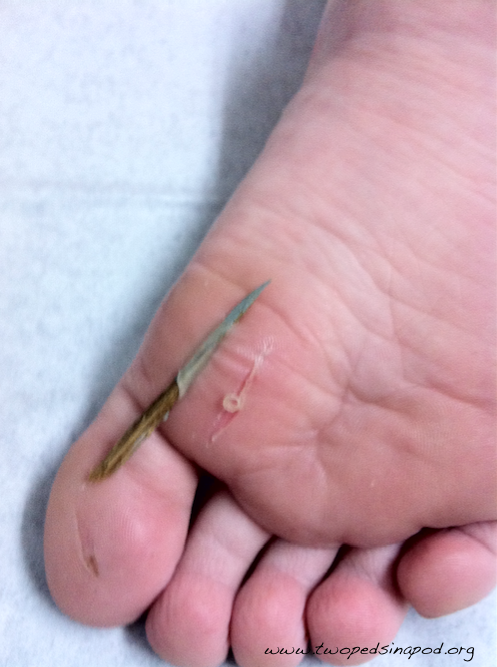
Sometimes a photo is worth a 1,000 words
Hopefully a splinter of the size in the photo is not lurking on your deck this weekend. The only redeeming feature of a splinter this size is that it is easy to yank out.
More often than not, splinters are teensy-weensy and too small to grab with tweezers. If the splinters in your child’s foot are tiny, seem near the surface of the skin, and do not cause much discomfort, simply soak the affected area in warm soapy water several times a day for a few days. Fifteen minutes, twice a day for four days, works for most splinters. Our bodies in general dislike foreign invaders and try to evict them. Water will help draw out splinters by loosening up the skin holding the splinter. This method works well particularly for multiple hair-like splinters such as the ones obtained from sliding down an obstacle course rope. Oil-based salves such as butter will not help pull out splinters. However, an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream will help calm irritation and a benzocaine-based cream (for kids over two years of age) can help with pain relief.
If a splinter is “grab-able”, gently wash the area with soap and water and pat dry. Don’t soak an area with a “grab-able” wooden splinter for too long because the wood will soften and break apart. Next, wash your own hands and clean a pair of tweezers with rubbing alcohol. Then, grab hold of the splinter and with the tweezers pull smoothly. Take care to avoid breaking the splinter before it comes out.
If the splinter breaks or if you cannot easily grab the end because it does not protrude from the skin, you can sterilize a sewing needle by first boiling it for one minute and then cleaning with rubbing alcohol. Wash the area with the splinter well, then with the needle, pick away at the skin directly above the splinter. Use a magnifying glass if you have to, make sure you have good lighting, and for those middle-age parents like us, grab those reading glasses. Be careful not to go too deep, you will cause bleeding which makes visualization impossible. Continue to separate the skin until you can gently nudge the splinter out with the needle or grab it with your tweezers.
Since any break in the skin is a potential source of infection, after you remove the splinter, wash the wound well with soap and water. Flush the area with running water to remove any dirt that remains in the wound. See our post on wound care for further details on how to prevent infection. If the splinter is particularly dirty or deep, make sure your child’s tetanus shot is up to date. Also, watch for signs of infection over the next few days: redness, pain at the site, or thick discharge from the wound are all reasons to take your child to his doctor for evaluation.
Some splinters are just too difficult for parents to remove. If you are not comfortable removing it yourself of if your child can’t stay still for the extraction procedure, head over to your child’s doctor for removal.
Now you can add “surgeon” to your growing list of parental hats.
Julie Kardos, MD with Naline Lai, MD
©2012 , rev 2016, 2017 Two Peds in a Pod®
