It’s 6 a.m., you are running late for work and your kid is “kinda” sick. Can you send him to daycare?

Dr. Kardos and Dr. Lai and a little friend talk about “Too Sick for School? The Latest Guidelines for Staying Home” at DVAEYC’s annual conference for early childhood educators
Yesterday we reviewed with an audience of early childhood education teachers the latest medical guidelines* for excluding children from early childhood education centers. Here are some of the updates we shared with the teachers attending the annual DVAEYC conference held at University of Pennsylvania:
When should a child go home from daycare? Remember the overriding goals for exclusion:
- To expedite the child’s recovery
To prevent undue burden on teachers
To protect other children and teachers from disease
Following are the guidelines that most surprised our audience, as well as other highlights from our talk.
Pink eye (conjunctivitis)– most kids can remain in school
- “Pink eye” is like a “cold in the eye” and can be caused by virus, bacteria, or allergies.
- Just as kids with runny noses can still attend school, so too can kids with runny eyes.
- A child with pink eye does not need to be on antibiotic eye drops in order to attend school. The presence or absence of treatment does not factor into letting a child attend school.
- Any child with pink eye who suffers eye pain, inability to open an eye, or has so much discharge that she is uncomfortable, needs to go home.
- If there is an outbreak (two or more kids in a room), the center’s health care consultant or the department of health can give ideas on how to help prevent further spread
- Good hand washing technique prevents the spread of the contagious forms of pink eye (viral or bacterial).
 Fever – by itself, is not an automatic exclusion
Fever – by itself, is not an automatic exclusion
- For practical purposes, a fever (no matter how it is taken) in a child who is over 8 weeks old is a temperature of 101 degrees F. Therefore, 99 degrees F is NOT a fever, even if that number is higher than the child’s baseline temperature.
- If a child with a fever acts well and does not require extra attention from teachers, then that child is medically safe to stay in school. Sending him home is unlikely to protect others. Kids are contagious the day before a fever starts, so febrile kids most likely already exposed their class to the fever-proking illness the day before the fever came.
- If the fever causes the child to become dehydrated or makes the child too sleepy or miserable to participate in class, then that child should go home.
- Any baby two months of age or younger with a fever of 100.4 or higher needs immediate medical attention, even if he is not acting sick.
- If a child has not received the recommended immunizations for his age, then he needs to be excluded for fever until it is known that he does NOT have a vaccine preventable illness.
- If a child goes home with a fever, he does not need medical clearance to return to school.
- Read more details about fever and “fever phobia” here.
Head lice, while icky and make our heads itch just to think about them, carry no actual disease.
- The child with live lice should go home at regular dismissal time, receive treatment that night, and be allowed back in school the next day.
- By the time you see lice on a child’s head, they have been there for likely at least a month. So sending him home early from school only punishes the child, causes the parent to miss work needlessly, and does nothing to prevent spread.
- Lice survive off of heads for 1-2 days at most (they need blood meals, and die without them), so a weekend without people in school kills any lice left behind in the classroom by Monday morning.
- Lice do not jump or fly and thus need close head-to-head contact to spread, hence the reasons behind why your child’s center spaces matts at nap time a certain amount distance apart, and do not allow kids to share personal objects such as combs.
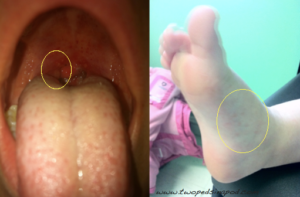
The mouth ulcers and foot rash of Hand Foot Mouth
Hand-foot-mouth disease- not an automatic exclusion
- This common virus, spread by saliva, causes a blister-like rash that can appear on hands, feet, in the mouth and in the diaper area, sometimes in all of these locations. Hand washing limits spread, and kids can attend school with this rash.
- The child who refuses to drink because of painful mouth lesions should go home so the parent can help improve hydration. In addition the child who refuses to participate in activities should stay home. You can read more about this virus here.
Poison ivy rash is not contagious to other people. The rash of poison ivy is an allergic reaction/irritation from wherever the oil of a poison plant touched the skin. The ONLY way to “catch” poison ivy is from the poison ivy plant itself. But if the itch from poison ivy makes a child too miserable to participate in class activities, she may need to go home. Read more about poison ivy here.
Vomiting more than twice, associated with other symptoms (such as fever, hives, dehydration or pain), or with vomit which is green-yellow or bloody are all reasons a child should leave school. Recent history of head injury warrants exclusion and immediate attention since vomiting can be a sign of bleeding in the head. See our post about vomiting.
Diarrhea, meaning an increase in stool frequency, or very loose consistency of stools, is a reason to go home if the diarrhea
- cannot be contained in a diaper,
- causes potty accidents in the toilet trained child
- contains blood, is bloody or black
- results in more than two stools above baseline for that child—too many diaper changes compromises the teacher’s ability to attend to other children.
- is with other symptoms such as fever, acting very ill or jaundiced (yellow skin/eyes)
- Read more about poop issues here.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign “only skin deep” illness similar to warts—direct vigorous contact or sharing of towels or bath water can spread the virus among kids but the rash itself is harmless and not a reason to stay home from school. Read our prior post for More on this little rash with the big name.
MRSA is a skin infection that looks red and pus filled and is typically painful for the child. Treatment involves draining the infection and/or taking oral antibiotics. If the infected area is small and can be covered completely, a child may stay in school.
Measles This illness causes high fever, cough, runny nose, runny eyes, and cough and a total body rash. Your local Department of Public Health will provide recommendations about how long to exclude a child with measles as well other precautions a school should take. So they are safe, unvaccinated children will have to be excluded for period of time as well.
Also note, at times, the department of public health will exclude even children who are acting well from school for outbreak management of a variety of infectious diseases.
Surprised? As you can see, there are few medical reasons to keep your child home from daycare for an extended period of time. As Dr. Lai often says to the big kids, “If there is nothing wrong with your brain, you can go to school and learn.” Bottom line- no matter the reason, if you realize at six in the morning that your child will not be able to learn and function at baseline, keep him home and seek the advice of your child’s pediatrician.
Julie Kardos, MD and Naline Lai, MD
©2017 Two Peds in a Pod®
*A straight-forward, comprehensive guide to the guidelines can be found in Managing Infectious Diseases in Child Care and Schools, 4th edition, Editors: Susan S. Aronson, MD, FAAP and Timothy R. Shope, MD, MPH, FAAP, published by the American Academy of Pediatrics.




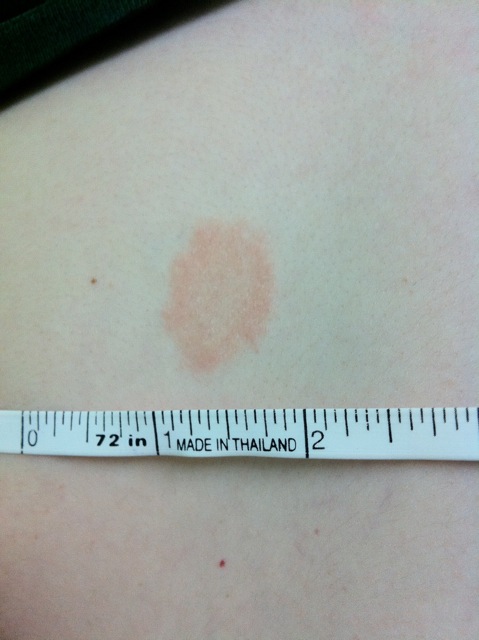 Although it’s called ringworm, this rash isn’t caused by a worm. In fact, it barely looks like a worm. Otherwise known as tinea corporis, the patch of ringworm is usually a flesh or light-pink colored, slightly scaly oval with raised, red edges.
Although it’s called ringworm, this rash isn’t caused by a worm. In fact, it barely looks like a worm. Otherwise known as tinea corporis, the patch of ringworm is usually a flesh or light-pink colored, slightly scaly oval with raised, red edges. 

 As we think about how to keep our parenting New Year’s resolutions, we find interesting advice from a fellow board member of
As we think about how to keep our parenting New Year’s resolutions, we find interesting advice from a fellow board member of 


